SQL Server Blog
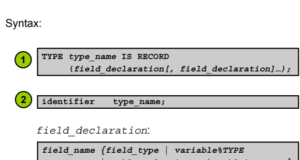
In Oracle PL/SQL, the %ROWTYPE attribute provides a record type representing a string in the Oracle database table (or view).A record may store an entire string of data selected from the...
Record type is a group of linked data elements stored in fields, each with its own name and data type. You can use Record as a variable, which may contain a table row or some columns (fields)...
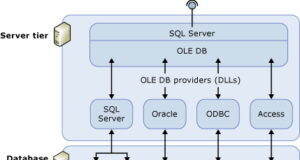
SQL Server has an interesting feature called Linked Servers. It is about linking other databases to SQL Server and using their data as local. There are many powerful open source systems written...
Thinking about security in MySQL installation, you can consider a wide range of possible procedures/recommendations and their impact on the security of your MySQL server and related...
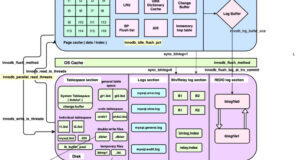
In this post we are going to share the MySQL 8 InnoDB architecture diagram with related variables.From the official MySQL document we have seen some InnoDB variables related to MySQL 8.0.20....
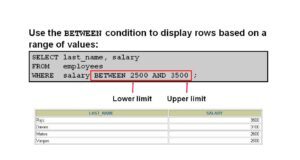
Oracle BETWEEN condition (also called BETWEEN operator) is used to obtain values within a range in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE sentences. Syntax of BETWEEN condition in...
Oracle IS NOT NULL condition is used to check for the value NOT NULL. You can use the Oracle condition IS NOT NULL either in an SQL sentence or in a block of PLSQL code. Syntax for IS NOT...
The Oracle IS NULL condition is used to check the NULL value. You can use the IS NULL condition either in an SQL sentence or in a block of PLSQL code. Syntax for IS NULL condition in...
The Oracle IN condition (also called the IN operator) determines whether a value or a list of values corresponds to an expression in the specified resulting SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE...
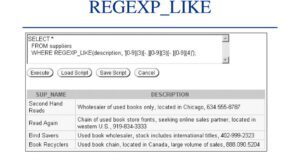
Oracle condition REGEXP_LIKE allows to execute regular expressions in WHERE proposal in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE queries. Syntax for REGEXP_LIKE in Oracle/PLSQL REGEXP_LIKE (...
Oracle condition LIKE allows to use wildcards which will be used in WHERE operator in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE queries. This allows comparison with a pattern. LIKE syntax in...
The Oracle NOT condition (also called NOT operator) is used to negate the condition in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE sentences. Syntax of the NOT condition in Oracle/PLSQL NOT...
Oracle AND and OR conditions can be combined in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE operators.When combining these conditions, it is important to use parentheses so that the database knows how...
The Oracle OR condition (also called the OR statement) is used to check several conditions in which records are returned when a particular condition is true. It can be used in SELECT, INSERT,...
Reflecting on security in MySQL installation, you can consider a wide range of possible procedures/recommendations and their impact on the security of your MySQL server and related...
In this post you will learn how to get the number of MySQL lines in a database. Getting the number of MySQL rows in one table To get the number of rows per table, you use the COUNT(*) operator...