REQUEST COMPLIMENTARY SQLS*PLUS LICENCE
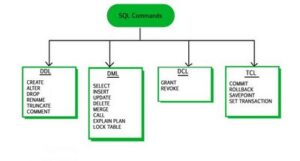
DDL / DML – SQL commands
DDL / DML – If you have an Oracle database and want to explore the capabilities of the FIRST_VALUE analytics function yourself, then below we provide the DDL and DML that you will need.
DDL (Data Definition Language) commands
DDL (Data Definition Language) commands are a subset of SQL used to define and modify various data structures. This group includes commands designed to create, modify and delete various database objects.
Commands CREATE (creation), ALTER (modification) and DROP (deletion) have most types of database objects (tables, views, procedures, triggers, table areas, users, etc.). I.e. there are many DDL commands such as CREATE TABLE, CREATE VIEW, CREATE PROCEDURE, CREATE TRIGGER, CREATE USER, CREATE ROLE, etc.
Some people think that the use of DDL is the prerogative of database administrators, and DML operators should be written by developers, but these two languages are not so easy to separate. It is difficult to organize affective data access and processing without understanding what structures are available and how they are connected. It is also difficult to design appropriate structures without knowing how they will be processed.
DCL (Data Control Language) commands
With the DCL (Data Control Language) commands, user access to the database can be controlled. Data control operators include the GRANT and REVOKE commands used to grant or deny permissions, and the SET ROLE command, which allows or prohibits roles for the current session.
TCL (Transaction Control language) commands
The commands of the transaction management language (TCL (Transactional Control Language)) allow you to determine the transaction outcome.
The commands of transaction management manage the changes in the database, which are performed by the data manipulation commands.
A transaction (or a logical unit of work) is an indivisible sequence of data manipulation operators (reading, deleting, inserting, modifying) from the point of view of affecting the database in such a way that either the results of all the operators included in the transaction are displayed in the database or the impact of all these operators is completely absent.
COMMIT – finishes (“confirms”) the current transaction and makes the alterations made by this transaction permanent (saves them in the database). It also deletes the saving points of this transaction and releases its locks. You can also use this command to manually confirm a doubtful distributed transaction.
ROLLBACK – performs transaction rollback, i.e. cancels all the changes made in the current transaction. It is also possible to use this command to manually undo the work performed by a dubious distributed transaction.
The concept of a transaction is directly related to the concept of database integrity. Very often a database can have such integrity restrictions that it is simply impossible not to break them by executing only one database alteration operator. For example, it is impossible to admit an employee to a department whose name and code is absent in the database.
In systems with advanced means of integrity limitation and control, each transaction begins with the integrity of the database and must leave this state holistic after its completion. Non-compliance with this condition leads to the fact that instead of fixing the results of the transaction is its rollback (ie, instead of the COMMIT operator is executed ROLLBACK), and the database remains in the state in which it was at the time of the beginning of the transaction, ie in an integral state.
Due to the property of maintaining the database integrity, transactions are suitable units of user isolation, i.e. if a transaction is associated with each database session, then each user starts working with the consistent database state, i.e. with the state in which the database could be located even if the user was working with it alone.
DML (Data manipulation language) commands
DML (Data Manipulation Language) commands allow the user to move data to and from the database:
- INSERT – performs row insertion into the table.
- DELETE – deletes rows from the table.
- UPDATE – performs modification of data in the table.
- SELECT – selects data from tables on request.
DDL example
DDL means the data definition language and is the instruction required to create the tables used in the FIRST_VALUE example.
Follow the following DDL:
CREATE TABLE employees( employee_id number_1(6) NOT NULL, f_name varchar2_1(25) NOT NULL, l_name varchar2_1(30) NOT NULL, salary number_1(8,2), department_id number_1(4), CONSTRAINT emp_id_pk PRIMARY KEY (employee_id));DML Example
DML means a data manipulation language. These are INSERT commands that you will need to run in your Oracle database to populate the data:
Run the following DML operators in your Oracle database:
insert intoemployees(empl_id,f_name,l_name,salary_1,depart_id)values (100,'Anita','Borg',2500,10);insert intoemployees(empl_id,f_name,l_name,salary_1,depart_id)values (200,'Alfred ','Aho',3200,10);insert intoemployees(empl_id,f_name,l_name,salary_1,depart_id)values (300,'Bill ','Gates',2100,10);insert intoemployees(empl_id,f_name,l_name,salary_1,depart_id)values (400,'Linus','Torvalds',3700,20);insert intoemployees(empl_id,f_name,l_name,salary_1,depart_id)values (500,'Michael','Dell',3100,20);insert intoemployees(empl_id,f_name,l_name,salary_1,depart_id)values (600,'Nello ','Cristianini',2950,20);insert intoemployees(empl_id,f_name,l_name,salary_1,depart_id)values (700,'Rasmus ','Lerdorf',4900,20);insert intoemployees(empl_id,f_name,l_name,salary_1,depart_id)values (800,'Steve','Jobs',2600,30);insert intoemployees(empl_id,f_name,l_name,salary_1,depart_id)values (900,'Thomas','Kyte',5000,30);
SQL Server – DDL and DML
MORE NEWS
PreambleNoSql is not a replacement for SQL databases but is a valid alternative for many situations where standard SQL is not the best approach for...
PreambleMongoDB Conditional operators specify a condition to which the value of the document field shall correspond.Comparison Query Operators $eq...
5 Database management trends impacting database administrationIn the realm of database management systems, moreover half (52%) of your competitors feel...
The data type is defined as the type of data that any column or variable can store in MS SQL Server. What is the data type? When you create any table or...
PreambleMS SQL Server is a client-server architecture. MS SQL Server process starts with the client application sending a query.SQL Server accepts,...
First the basics: what is the master/slave?One database server (“master”) responds and can do anything. A lot of other database servers store copies of all...
PreambleAtom Hopper (based on Apache Abdera) for those who may not know is an open-source project sponsored by Rackspace. Today we will figure out how to...
PreambleMongoDB recently introduced its new aggregation structure. This structure provides a simpler solution for calculating aggregated values rather...
FlexibilityOne of the most advertised features of MongoDB is its flexibility. Flexibility, however, is a double-edged sword. More flexibility means more...
PreambleSQLShell is a cross-platform command-line tool for SQL, similar to psql for PostgreSQL or MySQL command-line tool for MySQL.Why use it?If you...
PreambleWriting an application on top of the framework on top of the driver on top of the database is a bit like a game on the phone: you say “insert...
PreambleOracle Coherence is a distributed cache that is functionally comparable with Memcached. In addition to the basic function of the API cache, it...
PreambleIBM pureXML, a proprietary XML database built on a relational mechanism (designed for puns) that offers both relational ( SQL / XML ) and...
What is PostgreSQL array? In PostgreSQL we can define a column as an array of valid data types. The data type can be built-in, custom or enumerated....
PreambleIf you are a Linux sysadmin or developer, there comes a time when you need to manage an Oracle database that can work in your environment.In this...
PreambleStarting with Microsoft SQL Server 2008, by default, the group of local administrators is no longer added to SQL Server administrators during the...