REQUEST COMPLIMENTARY SQLS*PLUS LICENCE
Oracle Comparison Operators
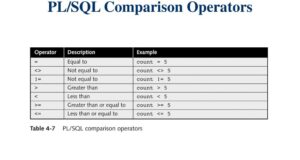
Comparison operators are used in the WHERE sentence to determine which records to select. Here is a list of comparison statements that you can use in Oracle PL/SQL:
| Comparator operators | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Exactly |
| <>, != | Whatever |
| > | More than |
| >= | More or equal |
| < | Less than |
| <= | Less or equal |
| IN ( ) | Corresponds to the value on the list |
| NOT | Negates the condition |
| BETWEEN | Within range (inclusive) |
| IS NULL | NULL value |
| IS NOT NULL | Value, not NULL |
| LIKE | Template matching % and _ |
| REGEXP_LIKE | Comparison of templates with regular expressions |
| EXISTS | This condition is fulfilled if the subquery returns at least one line |
Consider examples of comparison operators that you can use in Oracle PL/SQL.
Example of an equality operator
In Oracle PL/SQL you can use the = operator to verify equality in a query.
For example, you can use an = operator:
SELECT *
FROM contacts
WHERE last_name = 'Bernard';
In this example, the SELECT operator returns all the rows from the contacts table where last_name equals Bernard.
Here is an example of the inequality operator <>, !=
In Oracle PL/SQL, you can use the <> or != operators. To check inequality in a query.
For example, we could check for inequality using the <> operator in the following way:
SELECT *
FROM contacts
WHERE last_name <> 'Bernard';
In this example, the SELECT operator will return all the rows from the contacts table where last_name does not equal Bernard.
Or you may also write this query using the != operator in the following way:
SELECT *
FROM contacts
WHERE last_name != 'Bernard';
Both these requests will return the same results.
An example of an operator larger than >
You can use the > operator in Oracle PL/SQL to check the expression “more than”.
SELECT *
FROM contacts
WHERE contact_id > 20;
In this example, the SELECT statement will return all rows from the contacts table where contact_id is greater than 20. Contact_id equal to 20 will not be included in the result set.
Example operator greater than or equal to >=
In Oracle PL/SQL you can use the >= operator to check the expression, “more or equal”.
SELECT *
FROM contacts
WHERE contact_id >= 20;
In this example, the SELECT operator will return all rows from the contacts table where contact_id is greater than or equal to 20. In this case, contact_id equal to 20 will be included into the resulting set.
The example of the operator is less than <
You can use the < operator in Oracle PL/SQL to check the expression “less than”.
SELECT *
FROM contacts
WHERE contact_id < 150;
In this example, the SELECT operator will return all rows from the contacts table where contact_id is less than 150. contact_id equal to 150 will not be included in the resulting set.
The example of the operator is less than or equal to <=
In Oracle PL/SQL you can use the <= operator to check for an expression that is “less or equal”.
SELECT *
FROM contacts
WHERE contact_id <= 150;
In this example, the SELECT operator will return all rows from the contacts table where contact_id is less than or equal to 150. In this case, the product_id equal to 150 will be included into the resulting set.
Comparison Operators (Introduction to Oracle SQL)
MORE NEWS
PreambleNoSql is not a replacement for SQL databases but is a valid alternative for many situations where standard SQL is not the best approach for...
PreambleMongoDB Conditional operators specify a condition to which the value of the document field shall correspond.Comparison Query Operators $eq...
5 Database management trends impacting database administrationIn the realm of database management systems, moreover half (52%) of your competitors feel...
The data type is defined as the type of data that any column or variable can store in MS SQL Server. What is the data type? When you create any table or...
PreambleMS SQL Server is a client-server architecture. MS SQL Server process starts with the client application sending a query.SQL Server accepts,...
First the basics: what is the master/slave?One database server (“master”) responds and can do anything. A lot of other database servers store copies of all...
PreambleAtom Hopper (based on Apache Abdera) for those who may not know is an open-source project sponsored by Rackspace. Today we will figure out how to...
PreambleMongoDB recently introduced its new aggregation structure. This structure provides a simpler solution for calculating aggregated values rather...
FlexibilityOne of the most advertised features of MongoDB is its flexibility. Flexibility, however, is a double-edged sword. More flexibility means more...
PreambleSQLShell is a cross-platform command-line tool for SQL, similar to psql for PostgreSQL or MySQL command-line tool for MySQL.Why use it?If you...
PreambleWriting an application on top of the framework on top of the driver on top of the database is a bit like a game on the phone: you say “insert...
PreambleOracle Coherence is a distributed cache that is functionally comparable with Memcached. In addition to the basic function of the API cache, it...
PreambleIBM pureXML, a proprietary XML database built on a relational mechanism (designed for puns) that offers both relational ( SQL / XML ) and...
What is PostgreSQL array? In PostgreSQL we can define a column as an array of valid data types. The data type can be built-in, custom or enumerated....
PreambleIf you are a Linux sysadmin or developer, there comes a time when you need to manage an Oracle database that can work in your environment.In this...
PreambleStarting with Microsoft SQL Server 2008, by default, the group of local administrators is no longer added to SQL Server administrators during the...